In 2024, Locating Your Own Melodic Treasure Trove in YouTube's Vault

Locating Your Own Melodic Treasure Trove in YouTube’s Vault
YouTube Music has become a popular go-to platform for music lovers to find new songs and artists to enjoy. The content is uploaded regularly, so there’s always something new to discover.
But with so much music content on YouTube Music, finding the right mix for you can take time and effort. That’s why we’ve put together this guide on how to find my playlists on YouTube.
We’ll also answer some frequently asked questions to help you find solutions regarding the YouTube Mix queries. So, without wasting time, let’s get on with the guide!
Basic Information of YouTube Mix
Before starting, let’s learn some basic information about the YouTube Music Mix playlists:
Three Ways Of YouTube Music Mix
YouTube has popularized three personalized mixes to keep you up-to-date on newly released music and introduce more artists to you:
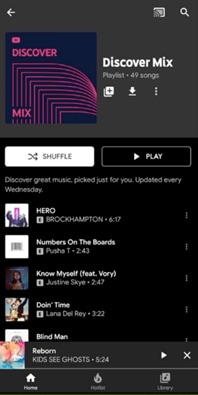
Discover Mix: Discover Mix introduces you to 50 new tracks every week, expanding your musical horizons and introducing you to contemporary artists. This playlist mix provides new updates every Wednesday, making it a go-to playlist for discovering new music to your taste.
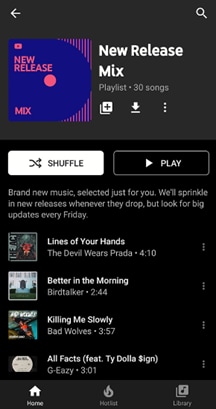
New Release Mix: In the New Release Mix playlist, you can find all the newest tracks from your favorite artists, and some music is recommended. New updates are provided every Friday (when most new releases come out), and mid-week releases the entire week to ensure you’re always up-to-date on the latest music.
Your Mix: Your Mix is a playlist full of songs by popular and well-known artists, as well as some new tunes and performers you’ve never discovered before, which are recommended based on your preferences, making it ideal for unwinding and listening to something you’re guaranteed to love. The playlist is updated regularly, so the music never gets dull, and there’s always something new to listen to.
What Is YouTube Music Replay Mix?
YouTube Music Replay Mix is a feature of YouTube Music that is automatically generated via the YouTube algorithm and contains a personalized mix of tracks based on your listening history. The mix is updated daily and includes up to 100 songs.
You can access it by tapping the “Replay Mix” option on the YouTube app’s main screen or the YouTube Music website. This feature is perfect for those who want a continuously updated mix of their favorite songs.
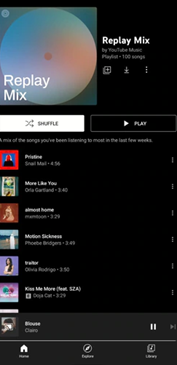
So, if you’re always on the go and need more time to create your playlist, YouTube Music Replay Mix is a great option. Since it’s based on your listening history, you can be sure that you’ll always hear songs that you love.
The Things You Want To Know About YouTube Mix
Now that you’ve what YouTube Mix is, you might have some queries in mind. To help you resolve them, we’ve provided solutions to the most frequently asked questions:
1. How Do I Save My Mix Playlist On YouTube?
To save My Mix playlist on YouTube, launch the YouTube app, tap “More” on the app’s main interface, and tap “Add to Library.” You can also save the playlist by going to the Mix page and tapping “Save” below the description.
2. How Do I Find My Playlist On YouTube?
The YouTube Music Replay Mix playlist is located on the home screen of the YouTube Music app and website under the “Mixed for you” header. Here you can also find other playlists, including “Your likes,” “New Release Mix,” “My Supermix,” and “Discover Mix.”
3. How Do I Add Songs To The Replay Mix Playlist?
You can’t manually add songs to the Replay Mix because YouTube Music automatically adds tracks that you listen to more than once.
The more often you hear a soundtrack, the higher it will appear on the YouTube list. Conversely, songs you’ve only played once or twice will appear lower on the list.
4. How Do I Delete A Mix Playlist On YouTube?
To delete a saved YouTube playlist from the Music library:
- Launch YouTube Music app on your mobile device or head to its website on your computer.
- Tap “Library” on the home screen or homepage and tap the “Mix” you want to delete.
- Tap the**”More”** option on the playlist panel and tap “Remove Playlist From Library.”
5. How Do I Turn Off YouTube Mixes?
To turn off YouTube Mixes, you can use Google extensions or create one yourself if you are an expert in coding.
6. Are YouTube Mixes Endless?
YouTube Music offers an endless personalized music playlist called “My Mixes.” Every time you click or tap the playlist, a new queue of your most listened or favorite tracks is generated for you.
The playlist contains about 100 songs with an endless auto-play feature once you reach the end of the list.
A Bonus Tip: How To Make a Music Video?
Hopefully, you have got the information you need about YouTube Mixes. Supposing you are YouTube music lover, we wonder, do you want to create YouTube videos for your channel or add music to your clips? In that case, we prepared a video tutorial for you - How To Make a Music Video. If you have any interests, you can watch it and learn about how to use the user-friendly video editor to make it:
Here’s why Wondershare Filmora is an excellent option for making YouTube videos or adding music to them:
- Huge royalty-free music library
- Easy to use, even for novice users
- Record videos from your webcam and screen simultaneously
- Multiple advanced video editing features, such as green screen, background blur, keyframe, split screen, motion tracking, and preset templates
- Adds effects, filters, transitions, and animations to your video footage to make it more eye-catching
- Quick “export to YouTube” feature to help you instantly share your final project on your channel
Free Download For Win 7 or later(64-bit)
Free Download For macOS 10.14 or later
If you want additional guidance on adding YouTube Music to your videos using Filmora,click here to learn everything you need to know!
Conclusion
This comprehensive guide explored some basic information about YouTube Music Mix and discussed how to find My Playlist on YouTube Music quickly. We’ve also provided solutions to help you save, find, delete, or turn off YouTube Mix playlists.
In addition, we’ve provided a bonus tip to use Filmora to add music to your YouTube videos and discussed its key features.
Hopefully, you’ve found this article helpful and can now locate your YouTube Music Mix playlist without issues.
Here’s why Wondershare Filmora is an excellent option for making YouTube videos or adding music to them:
- Huge royalty-free music library
- Easy to use, even for novice users
- Record videos from your webcam and screen simultaneously
- Multiple advanced video editing features, such as green screen, background blur, keyframe, split screen, motion tracking, and preset templates
- Adds effects, filters, transitions, and animations to your video footage to make it more eye-catching
- Quick “export to YouTube” feature to help you instantly share your final project on your channel
Free Download For Win 7 or later(64-bit)
Free Download For macOS 10.14 or later
If you want additional guidance on adding YouTube Music to your videos using Filmora,click here to learn everything you need to know!
Conclusion
This comprehensive guide explored some basic information about YouTube Music Mix and discussed how to find My Playlist on YouTube Music quickly. We’ve also provided solutions to help you save, find, delete, or turn off YouTube Mix playlists.
In addition, we’ve provided a bonus tip to use Filmora to add music to your YouTube videos and discussed its key features.
Hopefully, you’ve found this article helpful and can now locate your YouTube Music Mix playlist without issues.
Best Approach for Managing CC Rights & Usage
How to Use Creative Commons Copyright Licenses [Complete Guide]

Richard Bennett
Oct 26, 2023• Proven solutions

You might have noticed that, when you post a video, you get to choose how you want to copyright it: standard license, or creative commons. You’ve also probably noticed that when you looking for royalty-free music or stock footage a lot of it is licensed through creative commons.
So, what exactly are creative commons ?
To hold the copyright to a creative work means that you own it, and anybody who wants to use your work for anything (i.e. uses a song you composed in their YouTube video) has to do so on your terms. When you license your work through creative commons you do not give up your rights to your creative work (a common misconception).
When you use a creative commons license you are outlining the terms under which other creators are allowed to use your creations in their projects for free if they credit you for your work.
If you do not want anyone using your work for free in any context, you stick to traditional copyrighting.
But if you’ve created a piece of music, a photograph, or a clip that you wouldn’t mind other people using, potentially as a way to get your name out there, you might want to consider creative commons.
There are 6 different creative commons licenses. Which is right for you will depend on your answers to these two questions:
Are you okay with a creator making money off of something they create using your work?
Are you okay with a creator producing a derivative of your work?
To say ‘no derivatives’ is to say ‘I’m okay with people using it, so long as they don’t change it’. One example of a derivative is a techno remix of a song. If you are alright with other creators making derivatives of your work, you may also want to require them to ‘ShareAlike’. ShareAlike means that the creator of that techno remix of your song has to use the same creative commons license you used for your original to distribute the remix.
An example of a derivative someone might make of a YouTube video would be auto-tuning it to make a song or cutting up your video to make one that’s just ‘the funny parts’.
Here are the 6 creative commons licenses, and a chart you can use as a quick reference tool.
Attribution – CC BY
If you’re using music or other media with this license, all you need to do is credit the artist.
If you license your video this way, people can do whatever they like with any element of it (video or sound) so long as they credit you. I.e. if someone wanted to mute your clips and use you as stock footage in a bigger project, they could.
Attribution-ShareAlike – CC BY-SA
If you use music, photos, or any other media licensed this way, then you must both credit the artist and license your video this same way. Meaning, you can’t use YouTube’s standard license and must instead allow for others to use your work the way you are using the licensed media.
If you apply this license to your video, you’re saying you don’t mind people using all or portions of your video for their project so long as they allow others to use their work in the same way.
Attribution-NoDerivs – CC BY-ND
This one can get tricky.
Essentially, you can use media licensed this way so long as you don’t alter it or create a different version. For example, you can’t take a song licensed this way and use it in a mashup with another song. That part is clear. Where it gets tricky is when you want to use a song in your video.
Under normal copyright rules, using a royalty-free song in the background of your video would not count as creating a derivative. The definition of derivative according to creative commons is a bit broader and includes ‘syncing’. This means you can’t take an ‘Attribution-NoDerivs’ song and create any kind of music video for it.
For example, you can’t edit clips of yourself snowboarding so that they’re in sync with a song that has this license.
Whether or not you can play the song in the background of your vlog while you are speaking can be a bit of a grey area. In theory, it shouldn’t be a problem, but if you’re accessing the music through a social site like SoundCloud then it might be best to ask the artist first.
There’s no reason to license your YouTube videos this way. If people cannot alter your video, all that’s left is for them to repost it. Even though they’d also be crediting you, they’d still essentially be stealing views and ad revenue from your original video.
Attribution-NonCommercial – CC BY-NC
If you’re using stock footage, music, or stock photos licensed this way then you should still be able to monetize your video. YouTube monetization and commercial use are different things. However, there is a lot of confusion about this issue, and chances are the rights holder intends for this license to mean ‘no monetization’.
What you definitely could not do with a NonCommercial license is to use the song/other media in an actual commercial for a product, including product placement that a brand is paying you for.
If you license your video this way, people can use it in whatever way they like so long as they credit you and don’t try to make money off of it. Once again, that doesn’t mean they can’t use it in a YouTube video which they monetize because, technically, they’d be making money off of the ad that ran ahead of the video and not the video itself.
The thing to be careful of with this license is that it’s not ‘ShareAlike’. So, if you license your video this way somebody could use your clips as stock footage and then provide them - as part of their project – for free to a third person to use in a project they were making money off of.
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike – CC BY-NC-SA
Music and other media with an ‘Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike’ license can be used in and altered for your videos, so long as you aren’t making money off those videos. You must also use this same license for the video you create using elements licensed this way.
If you license your video this way, people can use it or a portion of it in their project if they credit you. They must also use this same license for their video if they do. This protects you from the situation where a third person who never licensed your original content is making money off of it.
Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs – CC BY-NC-ND
There aren’t many situations where you would be using media licensed this way in your YouTube videos. You can’t alter it, sync videos to it, or make money from any video that uses it.
You also probably shouldn’t use this license for your videos. ‘NoDerivs’ means there are not many ways people could use your content, except to repost full videos and steal your views.
Edit Video with the Most Excellent Video Editor

Richard Bennett
Richard Bennett is a writer and a lover of all things video.
Follow @Richard Bennett
Richard Bennett
Oct 26, 2023• Proven solutions

You might have noticed that, when you post a video, you get to choose how you want to copyright it: standard license, or creative commons. You’ve also probably noticed that when you looking for royalty-free music or stock footage a lot of it is licensed through creative commons.
So, what exactly are creative commons ?
To hold the copyright to a creative work means that you own it, and anybody who wants to use your work for anything (i.e. uses a song you composed in their YouTube video) has to do so on your terms. When you license your work through creative commons you do not give up your rights to your creative work (a common misconception).
When you use a creative commons license you are outlining the terms under which other creators are allowed to use your creations in their projects for free if they credit you for your work.
If you do not want anyone using your work for free in any context, you stick to traditional copyrighting.
But if you’ve created a piece of music, a photograph, or a clip that you wouldn’t mind other people using, potentially as a way to get your name out there, you might want to consider creative commons.
There are 6 different creative commons licenses. Which is right for you will depend on your answers to these two questions:
Are you okay with a creator making money off of something they create using your work?
Are you okay with a creator producing a derivative of your work?
To say ‘no derivatives’ is to say ‘I’m okay with people using it, so long as they don’t change it’. One example of a derivative is a techno remix of a song. If you are alright with other creators making derivatives of your work, you may also want to require them to ‘ShareAlike’. ShareAlike means that the creator of that techno remix of your song has to use the same creative commons license you used for your original to distribute the remix.
An example of a derivative someone might make of a YouTube video would be auto-tuning it to make a song or cutting up your video to make one that’s just ‘the funny parts’.
Here are the 6 creative commons licenses, and a chart you can use as a quick reference tool.
Attribution – CC BY
If you’re using music or other media with this license, all you need to do is credit the artist.
If you license your video this way, people can do whatever they like with any element of it (video or sound) so long as they credit you. I.e. if someone wanted to mute your clips and use you as stock footage in a bigger project, they could.
Attribution-ShareAlike – CC BY-SA
If you use music, photos, or any other media licensed this way, then you must both credit the artist and license your video this same way. Meaning, you can’t use YouTube’s standard license and must instead allow for others to use your work the way you are using the licensed media.
If you apply this license to your video, you’re saying you don’t mind people using all or portions of your video for their project so long as they allow others to use their work in the same way.
Attribution-NoDerivs – CC BY-ND
This one can get tricky.
Essentially, you can use media licensed this way so long as you don’t alter it or create a different version. For example, you can’t take a song licensed this way and use it in a mashup with another song. That part is clear. Where it gets tricky is when you want to use a song in your video.
Under normal copyright rules, using a royalty-free song in the background of your video would not count as creating a derivative. The definition of derivative according to creative commons is a bit broader and includes ‘syncing’. This means you can’t take an ‘Attribution-NoDerivs’ song and create any kind of music video for it.
For example, you can’t edit clips of yourself snowboarding so that they’re in sync with a song that has this license.
Whether or not you can play the song in the background of your vlog while you are speaking can be a bit of a grey area. In theory, it shouldn’t be a problem, but if you’re accessing the music through a social site like SoundCloud then it might be best to ask the artist first.
There’s no reason to license your YouTube videos this way. If people cannot alter your video, all that’s left is for them to repost it. Even though they’d also be crediting you, they’d still essentially be stealing views and ad revenue from your original video.
Attribution-NonCommercial – CC BY-NC
If you’re using stock footage, music, or stock photos licensed this way then you should still be able to monetize your video. YouTube monetization and commercial use are different things. However, there is a lot of confusion about this issue, and chances are the rights holder intends for this license to mean ‘no monetization’.
What you definitely could not do with a NonCommercial license is to use the song/other media in an actual commercial for a product, including product placement that a brand is paying you for.
If you license your video this way, people can use it in whatever way they like so long as they credit you and don’t try to make money off of it. Once again, that doesn’t mean they can’t use it in a YouTube video which they monetize because, technically, they’d be making money off of the ad that ran ahead of the video and not the video itself.
The thing to be careful of with this license is that it’s not ‘ShareAlike’. So, if you license your video this way somebody could use your clips as stock footage and then provide them - as part of their project – for free to a third person to use in a project they were making money off of.
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike – CC BY-NC-SA
Music and other media with an ‘Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike’ license can be used in and altered for your videos, so long as you aren’t making money off those videos. You must also use this same license for the video you create using elements licensed this way.
If you license your video this way, people can use it or a portion of it in their project if they credit you. They must also use this same license for their video if they do. This protects you from the situation where a third person who never licensed your original content is making money off of it.
Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs – CC BY-NC-ND
There aren’t many situations where you would be using media licensed this way in your YouTube videos. You can’t alter it, sync videos to it, or make money from any video that uses it.
You also probably shouldn’t use this license for your videos. ‘NoDerivs’ means there are not many ways people could use your content, except to repost full videos and steal your views.
Edit Video with the Most Excellent Video Editor

Richard Bennett
Richard Bennett is a writer and a lover of all things video.
Follow @Richard Bennett
Richard Bennett
Oct 26, 2023• Proven solutions

You might have noticed that, when you post a video, you get to choose how you want to copyright it: standard license, or creative commons. You’ve also probably noticed that when you looking for royalty-free music or stock footage a lot of it is licensed through creative commons.
So, what exactly are creative commons ?
To hold the copyright to a creative work means that you own it, and anybody who wants to use your work for anything (i.e. uses a song you composed in their YouTube video) has to do so on your terms. When you license your work through creative commons you do not give up your rights to your creative work (a common misconception).
When you use a creative commons license you are outlining the terms under which other creators are allowed to use your creations in their projects for free if they credit you for your work.
If you do not want anyone using your work for free in any context, you stick to traditional copyrighting.
But if you’ve created a piece of music, a photograph, or a clip that you wouldn’t mind other people using, potentially as a way to get your name out there, you might want to consider creative commons.
There are 6 different creative commons licenses. Which is right for you will depend on your answers to these two questions:
Are you okay with a creator making money off of something they create using your work?
Are you okay with a creator producing a derivative of your work?
To say ‘no derivatives’ is to say ‘I’m okay with people using it, so long as they don’t change it’. One example of a derivative is a techno remix of a song. If you are alright with other creators making derivatives of your work, you may also want to require them to ‘ShareAlike’. ShareAlike means that the creator of that techno remix of your song has to use the same creative commons license you used for your original to distribute the remix.
An example of a derivative someone might make of a YouTube video would be auto-tuning it to make a song or cutting up your video to make one that’s just ‘the funny parts’.
Here are the 6 creative commons licenses, and a chart you can use as a quick reference tool.
Attribution – CC BY
If you’re using music or other media with this license, all you need to do is credit the artist.
If you license your video this way, people can do whatever they like with any element of it (video or sound) so long as they credit you. I.e. if someone wanted to mute your clips and use you as stock footage in a bigger project, they could.
Attribution-ShareAlike – CC BY-SA
If you use music, photos, or any other media licensed this way, then you must both credit the artist and license your video this same way. Meaning, you can’t use YouTube’s standard license and must instead allow for others to use your work the way you are using the licensed media.
If you apply this license to your video, you’re saying you don’t mind people using all or portions of your video for their project so long as they allow others to use their work in the same way.
Attribution-NoDerivs – CC BY-ND
This one can get tricky.
Essentially, you can use media licensed this way so long as you don’t alter it or create a different version. For example, you can’t take a song licensed this way and use it in a mashup with another song. That part is clear. Where it gets tricky is when you want to use a song in your video.
Under normal copyright rules, using a royalty-free song in the background of your video would not count as creating a derivative. The definition of derivative according to creative commons is a bit broader and includes ‘syncing’. This means you can’t take an ‘Attribution-NoDerivs’ song and create any kind of music video for it.
For example, you can’t edit clips of yourself snowboarding so that they’re in sync with a song that has this license.
Whether or not you can play the song in the background of your vlog while you are speaking can be a bit of a grey area. In theory, it shouldn’t be a problem, but if you’re accessing the music through a social site like SoundCloud then it might be best to ask the artist first.
There’s no reason to license your YouTube videos this way. If people cannot alter your video, all that’s left is for them to repost it. Even though they’d also be crediting you, they’d still essentially be stealing views and ad revenue from your original video.
Attribution-NonCommercial – CC BY-NC
If you’re using stock footage, music, or stock photos licensed this way then you should still be able to monetize your video. YouTube monetization and commercial use are different things. However, there is a lot of confusion about this issue, and chances are the rights holder intends for this license to mean ‘no monetization’.
What you definitely could not do with a NonCommercial license is to use the song/other media in an actual commercial for a product, including product placement that a brand is paying you for.
If you license your video this way, people can use it in whatever way they like so long as they credit you and don’t try to make money off of it. Once again, that doesn’t mean they can’t use it in a YouTube video which they monetize because, technically, they’d be making money off of the ad that ran ahead of the video and not the video itself.
The thing to be careful of with this license is that it’s not ‘ShareAlike’. So, if you license your video this way somebody could use your clips as stock footage and then provide them - as part of their project – for free to a third person to use in a project they were making money off of.
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike – CC BY-NC-SA
Music and other media with an ‘Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike’ license can be used in and altered for your videos, so long as you aren’t making money off those videos. You must also use this same license for the video you create using elements licensed this way.
If you license your video this way, people can use it or a portion of it in their project if they credit you. They must also use this same license for their video if they do. This protects you from the situation where a third person who never licensed your original content is making money off of it.
Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs – CC BY-NC-ND
There aren’t many situations where you would be using media licensed this way in your YouTube videos. You can’t alter it, sync videos to it, or make money from any video that uses it.
You also probably shouldn’t use this license for your videos. ‘NoDerivs’ means there are not many ways people could use your content, except to repost full videos and steal your views.
Edit Video with the Most Excellent Video Editor

Richard Bennett
Richard Bennett is a writer and a lover of all things video.
Follow @Richard Bennett
Richard Bennett
Oct 26, 2023• Proven solutions

You might have noticed that, when you post a video, you get to choose how you want to copyright it: standard license, or creative commons. You’ve also probably noticed that when you looking for royalty-free music or stock footage a lot of it is licensed through creative commons.
So, what exactly are creative commons ?
To hold the copyright to a creative work means that you own it, and anybody who wants to use your work for anything (i.e. uses a song you composed in their YouTube video) has to do so on your terms. When you license your work through creative commons you do not give up your rights to your creative work (a common misconception).
When you use a creative commons license you are outlining the terms under which other creators are allowed to use your creations in their projects for free if they credit you for your work.
If you do not want anyone using your work for free in any context, you stick to traditional copyrighting.
But if you’ve created a piece of music, a photograph, or a clip that you wouldn’t mind other people using, potentially as a way to get your name out there, you might want to consider creative commons.
There are 6 different creative commons licenses. Which is right for you will depend on your answers to these two questions:
Are you okay with a creator making money off of something they create using your work?
Are you okay with a creator producing a derivative of your work?
To say ‘no derivatives’ is to say ‘I’m okay with people using it, so long as they don’t change it’. One example of a derivative is a techno remix of a song. If you are alright with other creators making derivatives of your work, you may also want to require them to ‘ShareAlike’. ShareAlike means that the creator of that techno remix of your song has to use the same creative commons license you used for your original to distribute the remix.
An example of a derivative someone might make of a YouTube video would be auto-tuning it to make a song or cutting up your video to make one that’s just ‘the funny parts’.
Here are the 6 creative commons licenses, and a chart you can use as a quick reference tool.
Attribution – CC BY
If you’re using music or other media with this license, all you need to do is credit the artist.
If you license your video this way, people can do whatever they like with any element of it (video or sound) so long as they credit you. I.e. if someone wanted to mute your clips and use you as stock footage in a bigger project, they could.
Attribution-ShareAlike – CC BY-SA
If you use music, photos, or any other media licensed this way, then you must both credit the artist and license your video this same way. Meaning, you can’t use YouTube’s standard license and must instead allow for others to use your work the way you are using the licensed media.
If you apply this license to your video, you’re saying you don’t mind people using all or portions of your video for their project so long as they allow others to use their work in the same way.
Attribution-NoDerivs – CC BY-ND
This one can get tricky.
Essentially, you can use media licensed this way so long as you don’t alter it or create a different version. For example, you can’t take a song licensed this way and use it in a mashup with another song. That part is clear. Where it gets tricky is when you want to use a song in your video.
Under normal copyright rules, using a royalty-free song in the background of your video would not count as creating a derivative. The definition of derivative according to creative commons is a bit broader and includes ‘syncing’. This means you can’t take an ‘Attribution-NoDerivs’ song and create any kind of music video for it.
For example, you can’t edit clips of yourself snowboarding so that they’re in sync with a song that has this license.
Whether or not you can play the song in the background of your vlog while you are speaking can be a bit of a grey area. In theory, it shouldn’t be a problem, but if you’re accessing the music through a social site like SoundCloud then it might be best to ask the artist first.
There’s no reason to license your YouTube videos this way. If people cannot alter your video, all that’s left is for them to repost it. Even though they’d also be crediting you, they’d still essentially be stealing views and ad revenue from your original video.
Attribution-NonCommercial – CC BY-NC
If you’re using stock footage, music, or stock photos licensed this way then you should still be able to monetize your video. YouTube monetization and commercial use are different things. However, there is a lot of confusion about this issue, and chances are the rights holder intends for this license to mean ‘no monetization’.
What you definitely could not do with a NonCommercial license is to use the song/other media in an actual commercial for a product, including product placement that a brand is paying you for.
If you license your video this way, people can use it in whatever way they like so long as they credit you and don’t try to make money off of it. Once again, that doesn’t mean they can’t use it in a YouTube video which they monetize because, technically, they’d be making money off of the ad that ran ahead of the video and not the video itself.
The thing to be careful of with this license is that it’s not ‘ShareAlike’. So, if you license your video this way somebody could use your clips as stock footage and then provide them - as part of their project – for free to a third person to use in a project they were making money off of.
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike – CC BY-NC-SA
Music and other media with an ‘Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike’ license can be used in and altered for your videos, so long as you aren’t making money off those videos. You must also use this same license for the video you create using elements licensed this way.
If you license your video this way, people can use it or a portion of it in their project if they credit you. They must also use this same license for their video if they do. This protects you from the situation where a third person who never licensed your original content is making money off of it.
Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs – CC BY-NC-ND
There aren’t many situations where you would be using media licensed this way in your YouTube videos. You can’t alter it, sync videos to it, or make money from any video that uses it.
You also probably shouldn’t use this license for your videos. ‘NoDerivs’ means there are not many ways people could use your content, except to repost full videos and steal your views.
Edit Video with the Most Excellent Video Editor

Richard Bennett
Richard Bennett is a writer and a lover of all things video.
Follow @Richard Bennett
Also read:
- [New] Essential Tips for Organizing Zoom Sessions for 2024
- [New] Finding the Perfect Phrases for Gamers' Videos
- [New] Fixing Obscured Content on YouTube Platform
- [Updated] 2024 Approved The Comprehensible Method for iFunny Meme Downloads
- Eight Effective Ways to Get the Control Center Running Smoothly on iPhones Again
- Exploring the Remarkable Ease of Repairing the HMD Skyline Among Modern Mobile Devices
- In 2024, 6 Ways To Transfer Contacts From Tecno Camon 30 Pro 5G to iPhone | Dr.fone
- In 2024, Find Hotspots for Online Video Dialogue
- In 2024, How I Transferred Messages from Samsung Galaxy XCover 6 Pro Tactical Edition to iPhone 12/XS (Max) in Seconds | Dr.fone
- IPhone Techniques for Seamless Image-to-PDF Conversion
- Journey Into the Future with YouTube’s Top VR Cinematography for 2024
- Make Every Sound Count Comprehensive Guide to Free YouTube Video Transcriptions for 2024
- Title: In 2024, Locating Your Own Melodic Treasure Trove in YouTube's Vault
- Author: Thomas
- Created at : 2025-01-28 19:12:01
- Updated at : 2025-01-30 00:23:28
- Link: https://youtube-help.techidaily.com/in-2024-locating-your-own-melodic-treasure-trove-in-youtubes-vault/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.